Rhizostoma comments
Classification of rhizotoma:
Phylum - Coelenterata
Class - Scyphozoa
Order - Rhizostomae
Genus - Rhizostoma
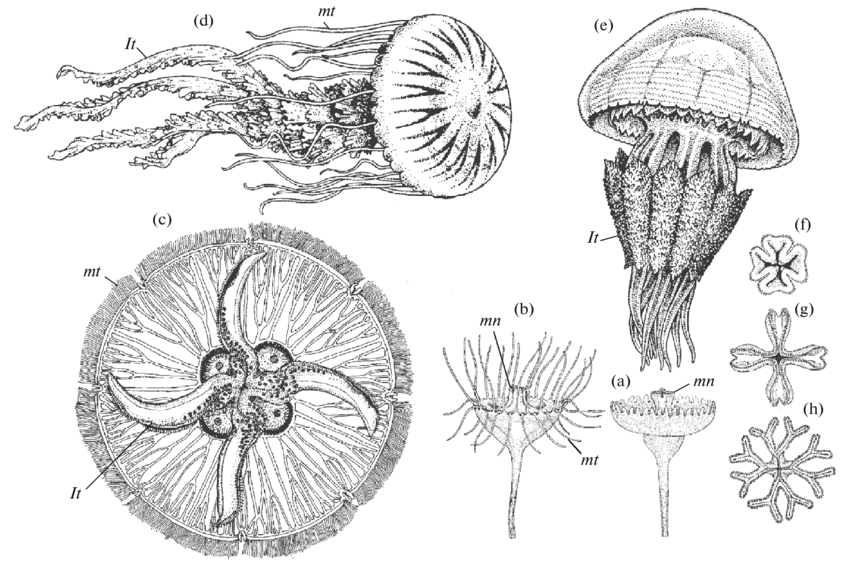 |
| Rhizostoma |
Habit and habitat:
Rhizostojna is a marine solitary medusoid Scyphozoa. It is a vigorous swimmer. Distribution: It is found in shallow waters in tropical and subtropical regions, especially Indo-pacific regions, North Carolina, and South Wales.
Comments:
(1) The body is hemispherical without marginal tentacles and divisible into ex-umbrellar and sub-umbrellar surfaces.
(2) Under sub-umbrella surface 8 fused oral
arms hang down in a central position.
(3) Oral arms are folded looking like root
in appearance called as scapulets. (4) The mouth is obliterated by the growth of oral arms which are modified as funnel-like securing pores called suctorial mouths.
(5) Each oral arm ends in a terminal
tentacle.
(6) The stomach is continued into canals, which open by funnel-shaped apertures on the edges of the arms.
(7) Young medusa has a single mouth which closes in the adult. (8) Entire animal has 96% water but does
not contain gelatin or mucilage. Feeds
on small fishes.
Identification: Since the specimen contains fused oral arms and all the above characters and hence it is
Rhizostoma
1. What is Rhizostoma?
- Rhizostoma is a genus of large, jellyfish-like marine organisms commonly known as "barrel jellyfish."
2. Where are Rhizostoma typically found?
- Rhizostoma jellyfish are primarily found in the coastal waters of the Atlantic Ocean, including the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea.
3. What is the size of Rhizostoma jellyfish?
- Rhizostoma jellyfish can reach impressive sizes, with some individuals having a bell diameter of up to one meter or more.
4. How do Rhizostoma jellyfish feed?
- Rhizostoma jellyfish are passive filter feeders, capturing small planktonic organisms and microscopic prey with their trailing tentacles.
5. Do Rhizostoma jellyfish have a sting?
- Yes, Rhizostoma jellyfish possess stinging cells called nematocysts in their tentacles. While their sting is generally mild and not harmful to humans, it can cause discomfort.
6. What is the distinctive appearance of Rhizostoma jellyfish?
- Rhizostoma jellyfish are characterized by their translucent, dome-shaped bells and a series of distinctive, cauliflower-like structures on their oral arms.
7. Are Rhizostoma jellyfish dangerous to swimmers?
- Rhizostoma jellyfish are generally not considered dangerous to humans, as their stings are usually mild and rarely cause serious harm. However, individuals with allergies or sensitive skin may experience more severe reactions.
8. What is the life cycle of Rhizostoma jellyfish?
- Rhizostoma jellyfish have a complex life cycle, including both a medusa (adult) stage and a polyp (larval) stage, which allows them to reproduce and grow.
9. How do Rhizostoma jellyfish reproduce?
- Reproduction in Rhizostoma jellyfish typically involves the release of eggs and sperm into the water, where fertilization occurs. The resulting larvae settle and develop into polyps, which eventually give rise to new medusae.
10. What role do Rhizostoma jellyfish play in marine ecosystems?
- Rhizostoma jellyfish play a role in marine ecosystems by controlling plankton populations through predation. Their presence can also provide food for certain marine species that prey on jellyfish, contributing to the marine food web.

No comments:
Post a Comment