Myxine
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Infraphylum: Agnatha
Class: Myxini
Order: Myxiniformes
Family: Myxinidae
Subfamily: Myxininae
Genus: Myxine
Linnaeus, 1758
 |
| Myxine |
Geographical distribution of Myxine
Myxine is distributed along seacoasts of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans in North European, North Atlantic, American, and Japanese sea waters.
Habit and habitat of Myxine
Hag fishes or Mahine sometimes descend to a depth of approximately 550 meters. Purely marine, nocturnal, and lie buried in the muddy bottom. Parasitic or quasiparasitic and generally found attached to the body of fishes, especially around the gill area. They bore their way into the host body to eat viscera and muscles..jpg)
Labeled diagram of myxine
Comments on Myxine
(1) Commonly called as hagfish or borer.
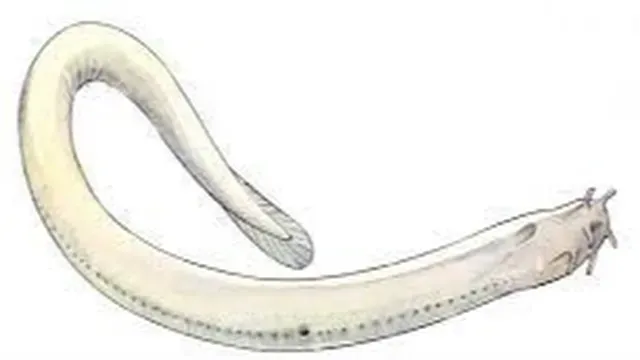
(2) Body soft, without scales, worm-like, measuring about 60 cm in length, and differentiated head, trunk, and tail.
(3) Anterior extremity contains four tentacles supported by skeletal rods.
(4) Mouth terminal and surrounded by lips. Buccal funnel and jaws are absent.
(5) Single nostril present close to the mouth. On ventrolateral sides mucous pores are distinct.
(6) Dorsal fin indistinct caudal fin and ventral fin confluents.
(7) Eyes vestigial, due to dark and bottom-dwelling habit, photoreceptor reduced. Secrete enormous mucus through mucous pores.
(8) 10 to 14 pairs of gills open into a branchial chamber, to open by a single branchial to the exterior.
(9) Hermaphroditic and protandrous. Eggs are enclosed in horny shells, bearing hooks that attach themselves to the weeds.
.jpg) |
| Labeled diagram of hagfish myxine |
Economic importance of Myxine
Hag fishes damage fishes entering into the nets. Sometimes hag fishes enter into the bodies of other fishes and eat entire soft parts leaving only a bag of skin and bones. Special features: Some individual produces sperm and then eggs later. Development direct. The hagfishes are injurious to the fish industry. They are important from an evolutionary point of view.
The evolution of jawed vertebrates from agnathans could be hypothesized as the latter needed only jaws. No direct link to understanding the evolution of gnathostomes, but some armored agnathan might have served as ancestors to the jawed vertebrates.
Identification of Myxine
Since the animal has 4 tentacles, a single gill aperture, no buccal funnel, and the above features, hence it is Myxine.
 |
| Myxine classification and characters |
REFERENCES
MCQs on Myxine
Let's solve some FAQs on myxine
1. By what name is the hagfish or borer commonly known?
They are commonly known as hagfish or borers.
2. Describe the structure of the body of a hag fish or borer.
- Their body is soft, scale-free, worm-like, and about 60 cm in length. It happens. They have a differentiated head, torso, and tail.
3. What is found in the front end of hagfish or borers?
The anterior end of the hagfish or borer has four tentacles supported by skeletal rods.
4. Where is the mouth located in hagfish or borers and what is its appearance?
- Hagfish or borers have a terminal mouth, surrounded by lips, and lack buccal funnels and jaws.
5. Which sensory organ is present near the mouth of hagfish or borers?
- Hagfish or borers have only one nostril near their mouth. Additionally, the mucous pores are distinct on the ventrolateral sides.
6. Describe the fins of a hagfish or a borer.
- Hagfish or borers have an indistinct dorsal fin, a caudal fin, and ventral fins that are fused.
7. How are the eyes of hagfish or borers affected by their habitat and habits?
- The eyes of the hagfish or borer are rudimentary (underdeveloped) due to their dark and bottom-dwelling habits. Fewer photoreceptors are the result of this adaptation.
8. How many pairs of gills do hagfish or borers have and where do they open?
- Hagfish or borers have 10 to 14 pairs of gills that open into a branchial chamber.
9. Describe the reproductive characteristics of hagfish or borers.
- Hagfish or borer are hermaphrodite and protandrous, which means they have both male and female reproductive organs. They start out as males and transition into females. Their eggs are encased in a horny shell and have hooks on them, which help them to attach to weeds.
10. How do hagfish or borer secrete substances?
- Hagfish or borers secrete heavy mucus through mucous pores.

No comments:
Post a Comment