Petromyzon
 |
| Petromyzon |
Classification
Class Cephalaspidomorphi – lampreys
Order Petromyzontiformes – lampreys, lampreas, lamproies
Family Petromyzontidae – lamproies, lampreas, lampreys
Genus Petromyzon Linnaeus, 1758
Species Petromyzon marinus Linnaeus, 1758 – sea lamprey, lamproie marine, lake lamprey
Geographical distribution
Petromyzon marinus is found in worldwide sea waters, coastal regions, streams, and lakes of North America, and Europe. West Africa, Australia, Chile, Japan, New Zealand, and Tasmania.
Habit and habitat of Petromyzon
Petromyzon is found both in salt and fresh water. They lead an ectoparasitic life on other fishes, attaching to the body of the host by buccal funnel and secreting an anticoagulant for continuous flow of blood. Anadromous ie, ascending river for spawning, carnivorous, and predators. .webp)
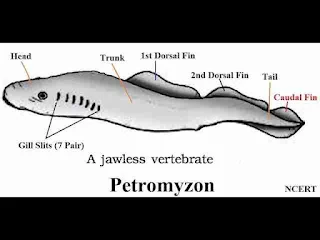
labeled diagram of Petromyzon
Comments on Pteromyzon
(1) Commonly called lamprey.
(2) Body eel-like, measuring about 90 cm, and differentiated into head, trunk, and tail. First dorsal fin, second dorsal fin and caudal fin confluent.
(3) Skin without scales, slimy, green, brown, and with a strong metallic luster.
(4) Head contains mouth but no jaws, Mouth surrounded by a large ventral suctorial funnel consisting of outer sensory cirri, oral fimbriae, marginal membrane, lateral bicuspid teeth, buccal funnel, mouth opening, tongue bearing piston like teeth, infra-oral teeth plate and horny teeth.
(5) Dorsal nasal sac and mouth are unconnected. Paired eyes are present behind the nasal aperture.
(6) Gill-slits are 7 pairs and the branchial basket is well developed.
(7) Sexes are separate. Female with large anal fin. Male with urinogenital or copulatory papilla. The development includes ammocoete larva which is very important phylogenetically as it is regarded as a connecting link between Amphioxus and cyclostomes.
Economic importance of Petromyzon
(i) Lampreys have very little food value, (ii) They injure and destroy fishes by sucking blood and causing a secondary infection, (iii) Larval lampreys are used as bait for sport fishing and commercial fishing. Special features: Lampreys are the lowest jawless vertebrates and their nearest allies are the ancient ostracoderms of the Silurian and Devonian periods. No fossil representatives of this group to indicate
Identification: Since the animal has 7 pairs of gill pores and is without jaws and has the above features, their course of evolution. hence it is Petromyzon.
Questions on Petromyzon
Q. What is the common name for Petromyzon?
Answer: Lamprey.
Q. How long is the body of Petromyzon?
Answer: Petromyzon is approximately 90 cm.
Q. Describe the skin of Petromyzon.
Answer: The skin is slimy, green, brown, and has a strong metallic luster. It lacks scales.
Q. What does the head of Petromyzon contain?
Answer: The head contains a mouth but no jaws. The mouth is surrounded by a large ventral suctorial funnel consisting of various structures.
Q. Are the dorsal nasal sac and mouth connected in Petromyzon?
Answer: No, they are unconnected. Paired eyes are present behind the nasal aperture.
Q. How many gill-slits does Petromyzon have?
Answer: Petromyzon has 7 pairs of gill-slits, and the branchial basket is well developed.
Q. Are Petromyzon individuals dioecious?
Answer: Yes, sexes are separate. Females have a large anal fin, while males have a urinogenital or copulatory papilla.
Q. What is the economic importance of Petromyzon?
Answer: (i) Lampreys have very little food value,
(ii) They injure and destroy fishes by sucking blood and causing secondary infection,
(iii) Larval lampreys are used as bait for sport fishing and commercial fishing.
Q. What is the special feature of Lampreys?
Answer: Lampreys are the lowest jawless vertebrates, and their closest relatives are the ancient ostracoderms of the Silurian and Devonian periods.
Q. How can Petromyzon be identified?
Answer: Petromyzon can be identified by having 7 pairs of gill pores, lacking jaws, and possessing the mentioned features.

No comments:
Post a Comment